CYBER SECURITY – Protect and Secure Your Data
CYBER SECURITY – Protect and Secure Your Data
Protect and Secure Your Data

Protect and Secure Your Data
Cyber security is the practice of defending computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks. It’s also known as information technology security or electronic information security. The term applies in a variety of contexts, from business to mobile computing, and can be divided into a few common categories.
- Network security is the practice of securing a computer network from intruders, whether targeted attackers or opportunistic malware.
- Application security focuses on keeping software and devices free of threats. A compromised application could provide access to the data its designed to protect. Successful security begins in the design stage, well before a program or device is deployed.
- Information security protects the integrity and privacy of data, both in storage and in transit.
- Operational security includes the processes and decisions for handling and protecting data assets. The permissions users have when accessing a network and the procedures that determine how and where data may be stored or shared all fall under this umbrella.
- Disaster recovery and business continuity define how an organization responds to a cyber-security incident or any other event that causes the loss of operations or data. Disaster recovery policies dictate how the organization restores its operations and information to return to the same operating capacity as before the event. Business continuity is the plan the organization falls back on while trying to operate without certain resources.
- End-user education addresses the most unpredictable cyber-security factor: people. Anyone can accidentally introduce a virus to an otherwise secure system by failing to follow good security practices. Teaching users to delete suspicious email attachments, not plug in unidentified USB drives, and various other important lessons is vital for the security of any organization.
The scale of the cyber threat
The global cyber threat continues to evolve at a rapid pace, with a rising number of data breaches each year. A report by RiskBased Security revealed that a shocking 7.9 billion records have been exposed by data breaches in the first nine months of 2019 alone. This figure is more than double (112%) the number of records exposed in the same period in 2018.
Medical services, retailers and public entities experienced the most breaches, with malicious criminals responsible for most incidents. Some of these sectors are more appealing to cybercriminals because they collect financial and medical data, but all businesses that use networks can be targeted for customer data, corporate espionage, or customer attacks.
With the scale of the cyber threat set to continue to rise, the International Data Corporation predicts that worldwide spending on cyber-security solutions will reach a massive $133.7 billion by 2022. Governments across the globe have responded to the rising cyber threat with guidance to help organizations implement effective cyber-security practices.
In the U.S., the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has created a cyber-security framework. To combat the proliferation of malicious code and aid in early detection, the framework recommends continuous, real-time monitoring of all electronic resources.
The importance of system monitoring is echoed in the “10 steps to cyber security”, guidance provided by the U.K. government’s National Cyber Security Centre. In Australia, The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) regularly publishes guidance on how organizations can counter the latest cyber-security threats.
Types of cyber threats

Cyber threats – Cybercrime, Cyber-attack, Cyberterrorism
The threats countered by cyber-security are three-fold:
- Cybercrime includes single actors or groups targeting systems for financial gain or to cause disruption.
- Cyber-attack often involves politically motivated information gathering.
- Cyberterrorism is intended to undermine electronic systems to cause panic or fear.
So, how do malicious actors gain control of computer systems? Here are some common methods used to threaten cyber-security:
Malware
Malware means malicious software. One of the most common cyber threats, malware is software that a cyber criminal or hacker has created to disrupt or damage a legitimate user’s computer. Often spread via an unsolicited email attachment or legitimate-looking download, malware may be used by cybercriminals to make money or in politically motivated cyber-attacks.
There are a number of different types of malware, including:
- Virus: A self-replicating program that attaches itself to clean file and spreads throughout a computer system, infecting files with malicious code.
- Trojans: A type of malware that is disguised as legitimate software. Cybercriminals trick users into uploading Trojans onto their computer where they cause damage or collect data.
- Spyware: A program that secretly records what a user does, so that cybercriminals can make use of this information. For example, spyware could capture credit card details.
- Ransomware: Malware which locks down a user’s files and data, with the threat of erasing it unless a ransom is paid.
- Adware: Advertising software which can be used to spread malware.
- Botnets: Networks of malware infected computers which cybercriminals use to perform tasks online without the user’s permission.
SQL injection
An SQL (structured language query) injection is a type of cyber-attack used to take control of and steal data from a database. Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in data-driven applications to insert malicious code into a databased via a malicious SQL statement. This gives them access to the sensitive information contained in the database.
Phishing
Phishing is when cybercriminals target victims with emails that appear to be from a legitimate company asking for sensitive information. Phishing attacks are often used to dupe people into handing over credit card data and other personal information.
Man-in-the-middle attack
A man-in-the-middle attack is a type of cyber threat where a cybercriminal intercepts communication between two individuals in order to steal data. For example, on an unsecure WiFi network, an attacker could intercept data being passed from the victim’s device and the network.
Denial-of-service attack
A denial-of-service attack is where cybercriminals prevent a computer system from fulfilling legitimate requests by overwhelming the networks and servers with traffic. This renders the system unusable, preventing an organization from carrying out vital functions.
Latest cyber threats
What are the latest cyber threats that individuals and organizations need to guard against? Here are some of the most recent cyber threats that the U.K., U.S., and Australian governments have reported on.
Dridex malware
In December 2019, the U.S. Department of Justice (DoJ) charged the leader of an organized cyber-criminal group for their part in a global Dridex malware attack. This malicious campaign affected the public, government, infrastructure and business worldwide.
Dridex is a financial trojan with a range of capabilities. Affecting victims since 2014, it infects computers though phishing emails or existing malware. Capable of stealing passwords, banking details and personal data which can be used in fraudulent transactions, it has caused massive financial losses amounting to hundreds of millions.
In response to the Dridex attacks, the U.K.’s National Cyber Security Centre advises the public to “ensure devices are patched, anti-virus is turned on and up to date and files are backed up”.
Romance scams
In February 2020, the FBI warned U.S. citizens to be aware of confidence fraud that cybercriminals commit using dating sites, chat rooms and apps. Perpetrators take advantage of people seeking new partners, duping victims into giving away personal data.
The FBI reports that romance cyber threats affected 114 victims in New Mexico in 2019, with financial losses amounting to $1.6 million.
Emotet malware
In late 2019, The Australian Cyber Security Centre warned national organizations about a widespread global cyber threat from Emotet malware.
Emotet is a sophisticated trojan that can steal data and also load other malware. Emotet thrives on unsophisticated password: a reminder of the importance of creating a secure password to guard against cyber threats.
End-user protection
End-user protection or endpoint security is a crucial aspect of cyber security. After all, it is often an individual (the end-user) who accidentally uploads malware or another form of cyber threat to their desktop, laptop or mobile device.
So, how do cyber-security measures protect end users and systems? First, cyber-security relies on cryptographic protocols to encrypt emails, files, and other critical data. This not only protects information in transit, but also guards against loss or theft.
In addition, end-user security software scans computers for pieces of malicious code, quarantines this code, and then removes it from the machine. Security programs can even detect and remove malicious code hidden in Master Boot Record (MBR) and are designed to encrypt or wipe data from computer’s hard drive.
Electronic security protocols also focus on real-time malware detection. Many use heuristic and behavioral analysis to monitor the behavior of a program and its code to defend against viruses or Trojans that change their shape with each execution (polymorphic and metamorphic malware). Security programs can confine potentially malicious programs to a virtual bubble separate from a user’s network to analyze their behavior and learn how to better detect new infections.
Security programs continue to evolve new defenses as cyber-security professionals identify new threats and new ways to combat them. To make the most of end-user security software, employees need to be educated about how to use it. Crucially, keeping it running and updating it frequently ensures that it can protect users against the latest cyber threats.
Cyber safety tips – protect yourself against cyber attacks
How can businesses and individuals guard against cyber threats? Here are our top cyber safety tips:
- Update your software and operating system: This means you benefit from the latest security patches.
- Use anti-virus software: Security solutions will detect and removes threats. Keep your software updated for the best level of protection.
- Use strong passwords: Ensure your passwords are not easily guessable.
- Do not open email attachments from unknown senders: These could be infected with malware.
- Do not click on links in emails from unknown senders or unfamiliar websites:This is a common way that malware is spread.
- Avoid using unsecure WiFi networks in public places: Unsecure networks leave you vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks.
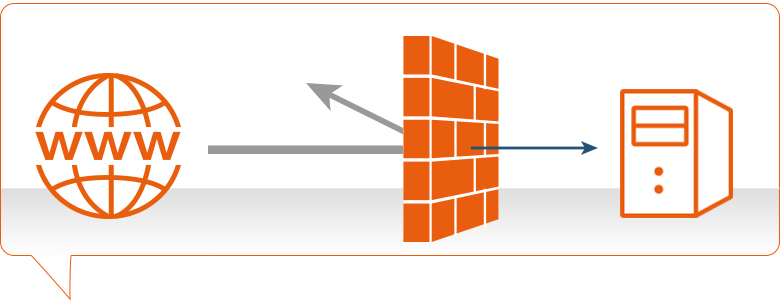
 Firewall Security Company India Complete Firewall Security Solutions Provider Company in India
Firewall Security Company India Complete Firewall Security Solutions Provider Company in India